Ethiopia’s Haile Gubbi volcano erupts after 12,000 years, spewing ash up to 14 km high
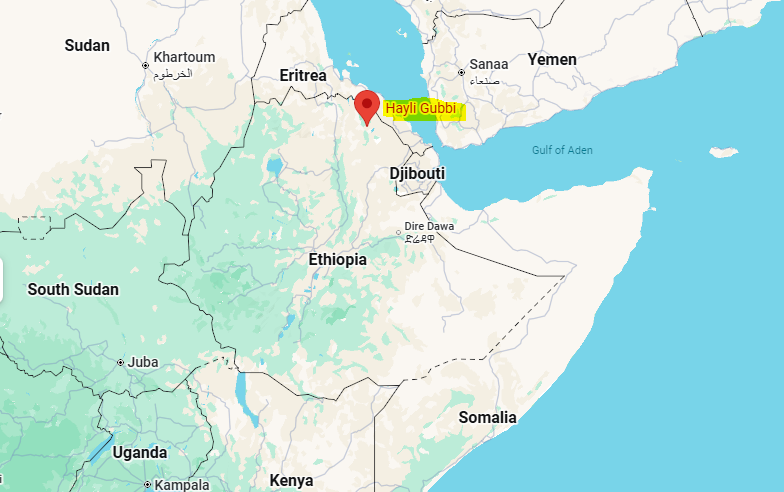
- The Hayli Gubbi volcano erupted on 23 November 2025 after nearly 12,000 years of dormancy. This volcano is located in Ethiopia’s Afar region, near the border of Ethiopia and Eritrea.
- The Afar region is part of the African Rift Valley, which is considered one of the most tectonically active regions on Earth.
- During the eruption, the volcano sent dense ash plumes up to about 14 kilometres into the atmosphere.
- According to the Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre, the volcanic ash drifted with the wind and reached Yemen, Oman, India and northern Pakistan.
- Satellite images clearly showed tall columnar structures of high-level ash rising from the crater of the volcano.
- Scientists have confirmed that there had been no recorded eruption of the Hayli Gubbi volcano during the Holocene period (the last 10–12 thousand years).
- The Global Volcanism Program of the Smithsonian Institution has also verified that there is no Holocene-era activity found in the historical records of this volcano.
- Residents living in nearby villages of Ethiopia reported heavy ash fall, although official information about casualties or displacement is not yet available.
- This rare eruption has alerted local authorities and global agencies to assess potential impacts on aviation routes, air quality and public health.
- Special monitoring and temporary adjustments are being made to international flight routes, as ash poses a serious hazard to aircraft.
- This event provides an important scientific opportunity to understand active geological processes and tectonic dynamics in the Afar region.

